|
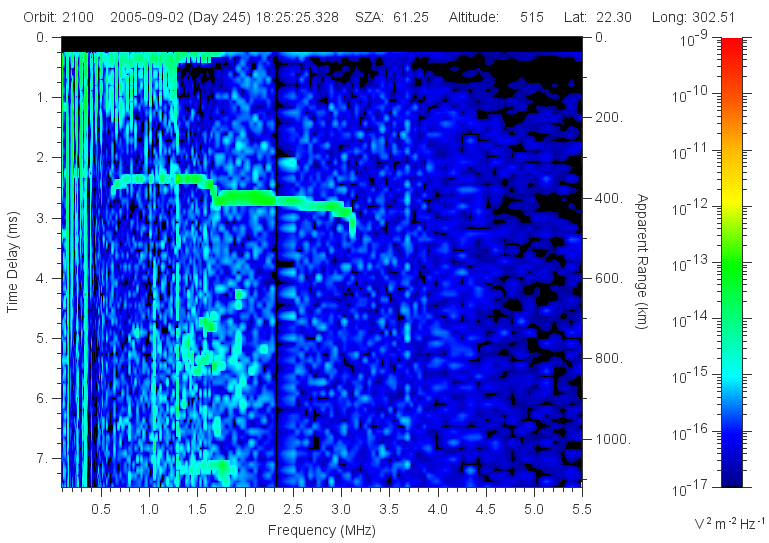
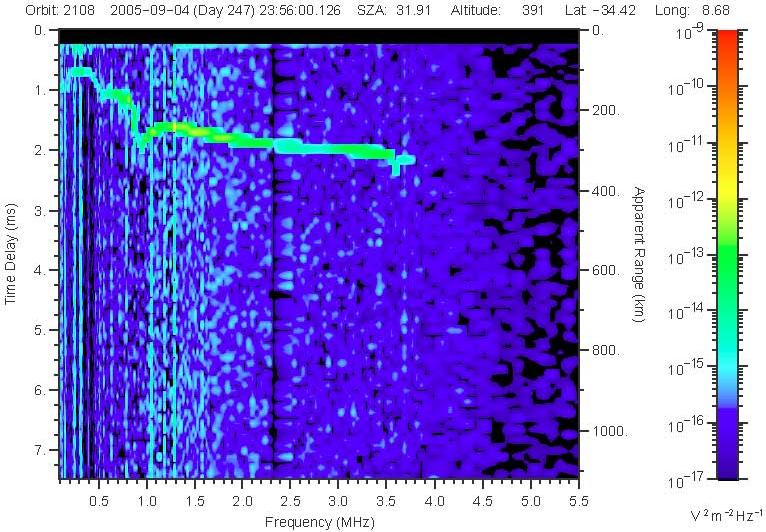
MARSIS data are analyzed using an ionogram, which plots the time delay of the
radar echo as a function of the frequency, color coded for amplitude. An
ionospheric radar echo appears as a trace exhibiting a smooth increase in time
delay with frequency and an intensity at least two orders of magnitude higher
than the background noise. As the frequency increases, this trace typically
displays an abrupt increase in time delay at some frequency, forming a
discontinuity in the trace that we call a "cusp". Cusps indicate locations of
maximums in the electron density as a function of altitude.
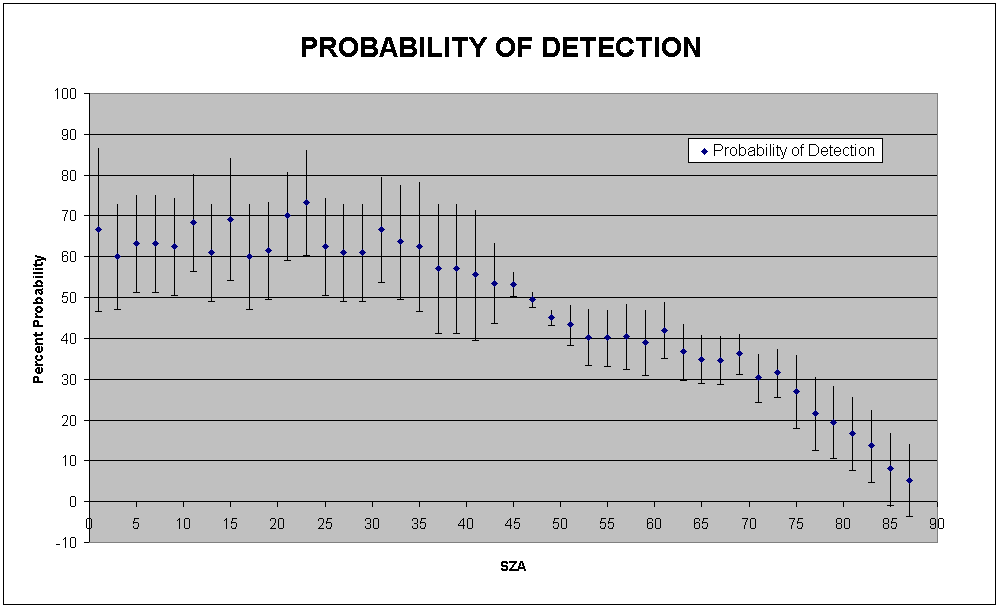
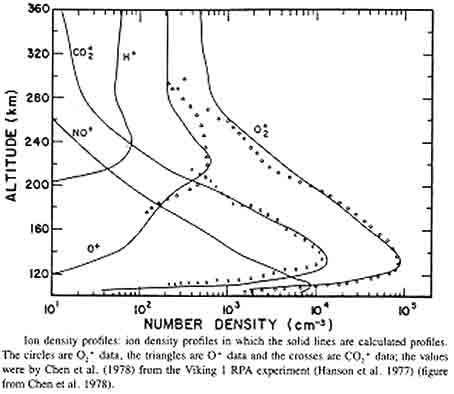
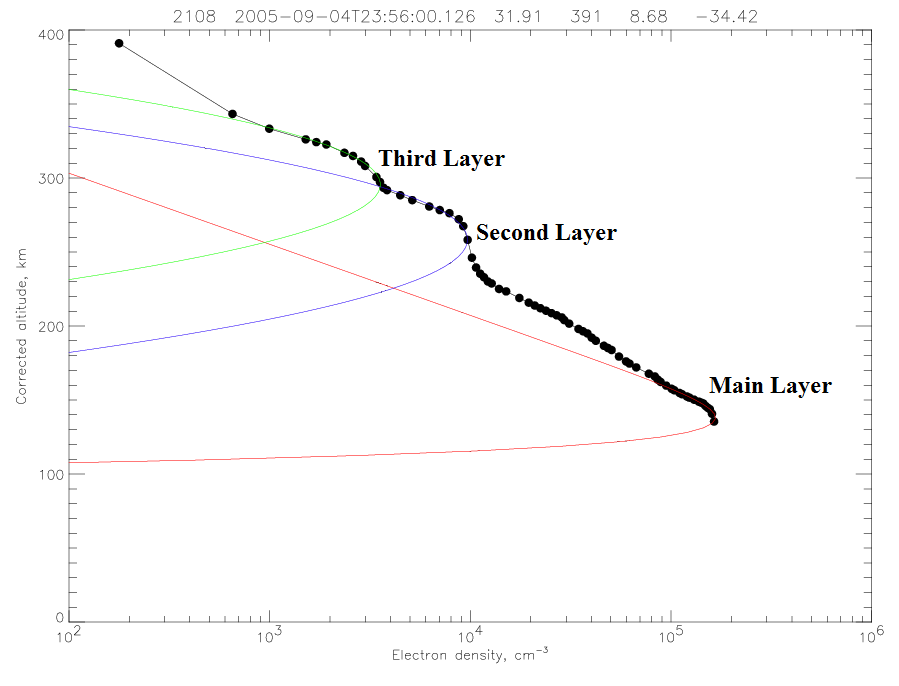
A rough estimate of the density profile can be obtained simply by using the apparent range to the reflection point; however, accurate measurements require correcting for dispersion in the ionospheric plasma. Since the time delay is known, the altitude as a function of the plasma frequency and, by conversion, the altitude as a function of the density can be computed for an assumed horizontally stratified ionosphere. Our approach to finding a density profile was to use a theoretical model and then adjust the parameters to give the best overall fit to the measurements. For a density model, we used the Chapman model from his 1931 paper. This fit yields the maximum density of the ionospheric layer, as well as the altitude at which this density occurs. Previous analysis has shown that the main Martian ionospheric layer has a cusp corresponding to a peak electron density of about 10^5 cm^-3 at an altitude of about 130 km, consistent with the results from the Viking landers of the 1970s showing that this main layer is primarily composed of O2+ and CO2+ ions. A summary of the results of the analysis of the main layer are published in a paper by Gurnett, et al (2005), and a new paper, with updated results and new findings, is in press and will be published in Advances in Space Research. |
|