 Part 3
Part 3
Even more important, the Earth Camera, which was designed to obtain global pictures of Earth's aurora, has produced abundant evidence that verifies the reality of signatures of these comets in images that Frank first obtained more than a decade earlier with NASA's Dynamics Explorer 1 (at right).
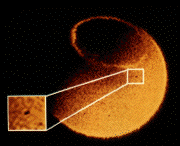 The images from the ultraviolet camera aboard the Dynamics Explorer
spacecraft contained black spots that Frank interpreted as being due to
clouds of cometary water vapor produced by the breakup of small comets.
Frank called these spots "atmospheric holes" because the
cometary clouds momentarily block Earth's dayglow, or sunlit
atmosphere, as seen by the camera aboard the spacecraft. The dayglow,
which is emitted by oxygen in our upper atmosphere, is light at
ultraviolet wavelengths beyond the range that can be seen by human eyes.
Frank's theory of a new class of objects in the solar system ignited a
wide-ranging controversy over the existence of these small comets or
whether the observations were "instrumental artifacts," as most
scientists concluded.
The images from the ultraviolet camera aboard the Dynamics Explorer
spacecraft contained black spots that Frank interpreted as being due to
clouds of cometary water vapor produced by the breakup of small comets.
Frank called these spots "atmospheric holes" because the
cometary clouds momentarily block Earth's dayglow, or sunlit
atmosphere, as seen by the camera aboard the spacecraft. The dayglow,
which is emitted by oxygen in our upper atmosphere, is light at
ultraviolet wavelengths beyond the range that can be seen by human eyes.
Frank's theory of a new class of objects in the solar system ignited a
wide-ranging controversy over the existence of these small comets or
whether the observations were "instrumental artifacts," as most
scientists concluded.